relational data model
- relation: 수학에서 나온 개념, 먼저 수학에서 relation이 의미하는 것이 무엇인지 파악해야 함.
- set: 서로 다른 elements를 가지는 collection, 즉 중복된 elements를 가지지 않음. 또한 하나의 set에서 elements의 순서는 중요하지 않음.

Cartesian product가 왜 중요한가?
수학에서 말하는 'relation'이 Cartesian product와 관련있기 때문.

이 3개의 pair들로 이루어진 집합은 A X B에 대한 Cartesian product의 부분 집합이 됨.
->이것이 수학에서 말하는 relation의 개념

n-ary relation은 n개의 집합에 대한 Cartesian product의 부분 집합이 됨.
relation in mathematics: subset of Cartesian product, set of tuples
-> 다시 말하면 수학에서 사용되는 relation의 개념은 Cartesian product의 부분 집합, 혹은 tuple들의 집합이다.
relational data model에서 수학에서의 relation의 개념이 어떻게 적용되는지 살펴보자.

- set을 바탕으로 수학에서 relation의 의미 파악함 -> relational data model에서 set은 domain을 의미함. (set -> domain)
- domain: 값들의 집합, 각 domain에 이름 붙일 수 있음
- tuple 가질 수 있음.
대학생 데이터를 저장하는 student를 relational data model에서 어떻게 relation으로 표현하는지 예를 통해 살펴보자.
먼저 student relation을 표현하기 위해서 관련된 domain부터 정의해보자.

위와 같이 정의된 domain을 바탕으로 relation을 만들어보자.

- phone_numbers: 학생의 전화번호를 저장할 뿐만 아니라, 그 학생의 비상 연락망도 저장함.
- 즉 동일한 domain이 같은 relation에서 두 번 사용되는 것임. 하지만 사용되는 목적, 역할이 다름.
- 이러한 역할을 표시해주기 위해서 relation data model에서 attribute라는 개념이 등장!
- 각각의 domain들이 relation에서 어떤 역할을 수행하는지, 수행하는 역할의 이름을 붙여주는 것이 attribute의 의미.

BUT, relational data model을 사용할 때 위와 같이 그림으로 잘 표현하지 않음.
이를 가장 잘 표현할 수 있는 것은 table!
그래서 relation을 table이라고 설명하는 것이다.
왜? relational data model에서 tuple들이 table로 잘 표현되기에.

- attribute: 각 도메인에 대해, relation안에서 부여된 역할 이름
- tuple: attribute 각각의 값들로 이루어진 리스트
- 이 전체를 relation이라 하고, 흔히 table이라고 많이 표현됨.
- 또한 relation에는 이름이 있음.
개념 정리하자면, 다음 그림과 같음

relation schema
- relation의 구조 나타냄
- relation 이름과 attributes 리스트로 표기됨 ex: STUDENT(id, name, grade, major, phone_num, emer_phone_num)
- 시각적으로 표기가 되진 않지만, attributes와 관련된 constraints도 포함됨
degree of a relation
- relation schema에서 attributes의 수
- ex: STUDENT(id, name, grade, major, phone_num, emer_phone_num) -> degree 6
relation의 또 다른 의미
- relation state: 임의의 시점에서의 tuple들의 집합
- relation이 개념적인 의미에서의 relation을 의미하는 것인지, tuple들의 집합으로서의 relation을 의미하는 것인지 문맥을 통해 잘 파악해야 할 것!
relational database
- relational data model에 기반하여 구조화된 database
- relational database는 여러 개의 relations으로 구성된다
relational database schema
- relational schemas set + (relation들 간의) integrity constraints set
relation 특징
- relation은 중복된 tuple을 가질 수 없다. (relation is set of tuples)
- relation의 tuple을 식별하기 위해 attribute의 부분 집합을 key로 설정한다. (ex: student relation에서는 id를 통해 각 tuple을 unique하게 식별함)
- relation에서 tuple의 순서는 중요하지 않다. (tuple들간의 순서가 바뀌어도 이 relation의 의미는 동일함)
- 하나의 relation에서 attribute의 이름은 중복되면 안된다.
- 하나의 tuple에서 attribute의 순서는 중요하지 않다.
- attribute는 atomic해야 한다 (composite or multivalued attribute 허용 안됨)

서울특별시 강남구 청담동: 서울특별시/강남구/청담동 으로 쪼개질 수 있는 attribute를 composite attribute라고 함
컴공, 디자인: multivalued attribute
NULL의 의미
- 값이 존재하지 않는다
- 값이 존재하나 아직 그 값이 무엇인지 알지 못한다
- 해당 사항과 관련이 없다
-> NULL은 중의적인 의미를 가짐. NULL 하나로 여러가지 의미가 표현되기에 최대한 NULL을 쓰지 않는 것이 좋음
keys
superkey: relation에서 tuples를 unique하게 식별할 수 있는 attributes set
ex) PLAYER(id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)의 super key는 여러가지 있을 수 있음.
- 전체 attribute set 즉, {id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date}을 가지면 그 자체가 super key가 됨. -> relation 정의 자체가 중복되는 tuple은 허용하지 않기에
- 선수들의 id와 name으로 이루어진 attribute set {id, name}도 super key가 됨 -> id 자체가 선수들의 고유 번호이기에 id를 포함하는 attribute set이면 어떤 것이든 super key가 됨
- {name, team_id, back_number}도 supker key가 됨 -> 서로 다른 팀에서는 같은 등 번호가 있을 수 있지만 같은 팀 내에서는 고유한 등 번호를 가짐. 또한 team마다 부여된 id는 고유할 것이기에 team id와 back_number를 통해 unique하게 식별할 수 있음. 이 둘을 포함한 어떤 attribute set이든 super key가 됨
candidate key (key or minimal superkey) : 어느 한 attribute라도 제거하면 unique하게 tuples를 식별할 수 없는 super key
ex: {id}, {team_id, back_number}
- {team_id, back_number}: team_id만으로 tuple을 unique하게 식별할 수 없음. 한 팀 내에서 여러 명의 선수가 있기에. 마찬가지로 back_number만으로 tuple을 unique하게 식별할 수 없음. 서로 다른 팀에 같은 등 번호를 가진 선수 있기에
primary key: relation에서 tuples를 unique하게 식별하기 위해 선택된 candidate key
ex: {id}
-> 보통 primary key를 고를 때는 attribute 숫자가 적은 걸로 고름
unique key (alternate key): primary key가 아닌 candidate keys
ex: {team_id, back_number}
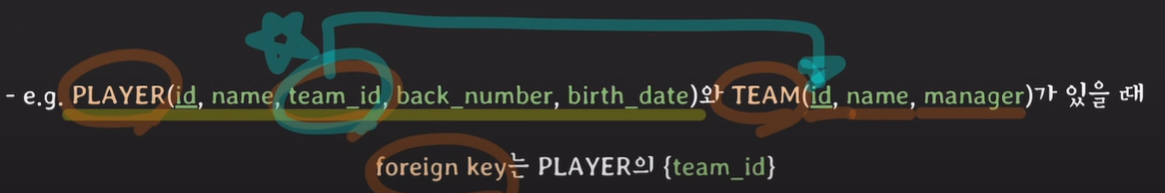
foreign key: 다른 relation의 PK를 참조하는 attributes set
constraints
: relational database의 relations들이 언제나 항상 지켜줘야 하는 제약 사항
- implicit constraints: relational data model 자체가 가지는 constraints (relation은 중복되는 tuple을 가질 수 없음, relation 내에서는 같은 이름의 attribute 가질 수 없음)
- schema-based constraints (explicit constraints): 주로 DDL을 통해 schema에 직접 명시할 수 있는 constraints
schema-based constraints 종류
- domain constraints: attribute의 value는 해당 attribute의 domain에 속한 value여야 함.

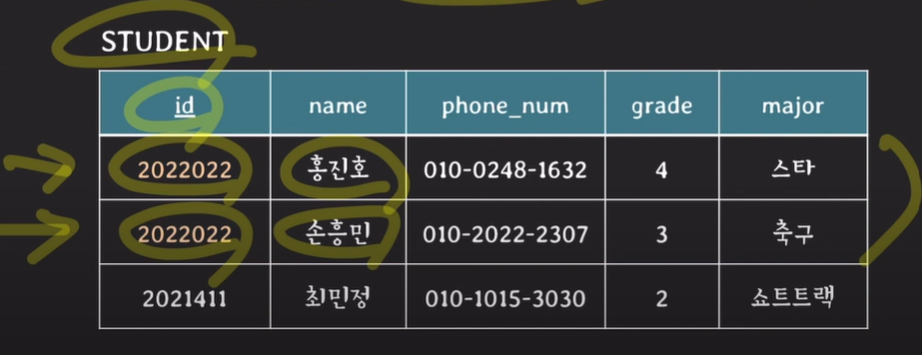
- key constraints: 서로 다른 tuples는 같은 value의 key를 가질 수 없다.
- NULL value constraint: attribute가 NOT NULL로 명시됐다면 NULL을 값으로 가질 수 없다

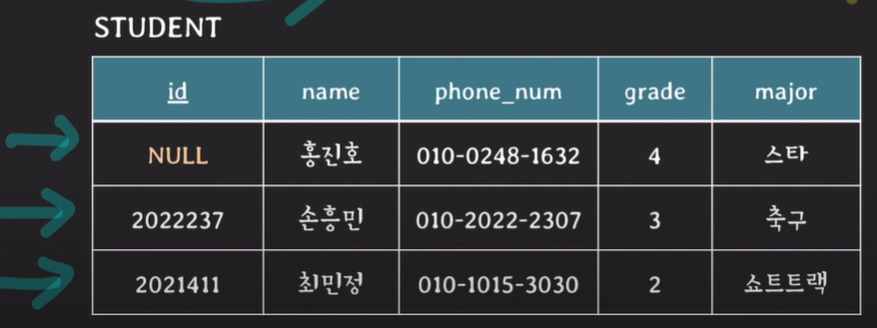
- entity integrity constraint: primary key는 value에 NULL을 가질 수 없다 (primary key는 tuple을 unique하게 식별하기 위해 사용되는 key인데, value가 NULL이 될 수 있다면 더 이상 tuple을 unique하게 식별할 수 없게 됨)
- referential integrity constraint: FK와 PK와 도메인이 같아야 하고 PK에 없는 values를 FK가 값으로 가질 수 없다

constraint를 두는 이유는 data의 일관성을 보장하기 위해 !
구현을 하다보면 constraint를 위반하는 경우 발생 -> constraint를 위반하는 값을 입력했다 등의 error를 받게 됨.



